If we take a step back, the automation platform will need to handle the following:
- The workflow is triggered on a regular basis (e.g. every 15-30 minutes) from n8n and logs are analyzed using Prometheus API. Additional logs from Loki are pulled for failing/inactive critical system services.
- AI makes a judgement on the severity and type of action that needs to be taken.
- Discord notification is fired up with a timeout respective to the level of risk.
- If approved (or is auto-passed on time out), Claude (or another AI of your choice) decides which playbook in AWX or Semaphore to run.
- n8n calls AWX or Semaphore UI API to launch one of the respective playbook per job. Each one of them can take
service_nameandtarget_hostas variables passed on from n8n to AWX:restart-service.ymlclear-disk-space.ymlreboot-host.ymlkill-process.yml
- AWX or Semaphore UI handle SSH, credentials, logging (this was already set up in a guide I referenced above).
- The n8n workflow waits for the results and informs the admin via Discord. Then loops back in case more issues were identified.
Create Ansible playbooks
- In your source version control tool, create a new folder (I called mine
ansible-remediation). See below for the structure:
ansible-remediation/
├── playbooks/
│ ├── restart-service.yml
│ ├── clear-disk-space.yml
│ ├── reboot-host.yml
│ ├── kill-process.yml
├── inventory/
│ └── (use existing dynamic inventory or add custom hosts)
└── README.mdPlaybook: restart-service.yml
---
# Restart a failed systemd service
# Variables: target_host, service_name
# Risk: LOW
- name: Restart Failed Service
hosts: "{{ target_host }}"
become: yes
gather_facts: no
vars:
max_retries: 3
retry_delay: 5
tasks:
- name: Check current service status
ansible.builtin.systemd:
name: "{{ service_name }}"
register: service_before
failed_when: false
- name: Fail if service does not exist
ansible.builtin.fail:
msg: "Service {{ service_name }} does not exist on {{ target_host }}"
when: service_before.status is not defined
- name: Restart the service
ansible.builtin.systemd:
name: "{{ service_name }}"
state: restarted
register: restart_result
failed_when: false
- name: Wait for service to stabilize
ansible.builtin.systemd:
name: "{{ service_name }}"
register: service_after
until: service_after.status.ActiveState in ['active', 'running']
retries: "{{ max_retries }}"
delay: "{{ retry_delay }}"
failed_when: false
- name: Set result fact
ansible.builtin.set_fact:
remediation_result:
success: "{{ service_after.status.ActiveState | default('unknown') in ['active', 'running'] }}"
service: "{{ service_name }}"
host: "{{ target_host }}"
state_before: "{{ service_before.status.ActiveState | default('unknown') }}"
state_after: "{{ service_after.status.ActiveState | default('failed') }}"
restart_attempted: "{{ restart_result is success }}"
message: "{{ 'Service ' + service_name + ' restarted successfully, now ' + (service_after.status.ActiveState | default('unknown')) if service_after.status.ActiveState | default('unknown') in ['active', 'running'] else 'Service ' + service_name + ' failed to restart, state: ' + (service_after.status.ActiveState | default('unknown')) }}"
- name: Output result
ansible.builtin.debug:
var: remediation_result
Playbook: clear-disk-space.yml
---
# Clean space on a drive & identify large files
# Variables: target_host
# Risk: LOW
---
- name: Clear disk space and analyze usage
hosts: "{{ target_host }}"
become: yes
tasks:
- name: Get disk usage before cleanup
command: df -h /
register: disk_before
- name: Find largest directories in /var
shell: du -sh /var/*/ 2>/dev/null | sort -rh | head -10
register: var_usage
ignore_errors: yes
- name: Find largest files over 100MB (ignore external storage)
ansible.builtin.shell: |
find / -xdev -type f -size +100M 2>/dev/null | head -20
async: 300 # 5 minute max
poll: 10
register: large_files
ignore_errors: yes
- name: Check apt cache size
shell: du -sh /var/cache/apt/archives 2>/dev/null || echo "0 /var/cache/apt/archives"
register: apt_cache
ignore_errors: yes
- name: Check journal size
shell: journalctl --disk-usage 2>/dev/null || echo "Journal size unknown"
register: journal_size
ignore_errors: yes
- name: Check docker disk usage
shell: docker system df 2>/dev/null || echo "Docker not installed"
register: docker_usage
ignore_errors: yes
- name: Clean apt cache
apt:
autoclean: yes
autoremove: yes
ignore_errors: yes
- name: Clean old journal logs
shell: journalctl --vacuum-time=7d
register: journal_cleaned
ignore_errors: yes
- name: Clean tmp files older than 7 days
shell: find /tmp -type f -mtime +7 -delete 2>/dev/null || true
ignore_errors: yes
- name: Clean old log files
shell: |
find /var/log -type f -name "*.gz" -mtime +30 -delete 2>/dev/null || true
find /var/log -type f -name "*.old" -delete 2>/dev/null || true
ignore_errors: yes
- name: Get disk usage after cleanup
command: df -h /
register: disk_after
- name: Display report
vars:
report_text: |
========== DISK CLEANUP REPORT ==========
BEFORE cleanup: {{ disk_before.stdout_lines[1] | default('unknown') }}
AFTER cleanup: {{ disk_after.stdout_lines[1] | default('unknown') }}
=== Top 10 directories in /var ===
{{ var_usage.stdout | default('Unable to scan') }}
=== Large files over 100MB ===
{{ large_files.stdout | default('None found') }}
=== Cache and Log sizes ===
APT Cache: {{ apt_cache.stdout | default('unknown') }}
Journal: {{ journal_size.stdout | default('unknown') }}
=== Docker usage ===
{{ docker_usage.stdout | default('Not available') }}
=== Cleanup actions performed ===
Journal vacuum: {{ journal_cleaned.stdout | default('skipped') }}
=== Recommendations ===
Review large files above for potential removal
Check /var/log for application-specific logs
Consider docker system prune if Docker usage is high
==========================================
debug:
msg: "{{ report_text }}"
Playbook: reboot-host.yml
---
# Reboot a host
# Variables: target_host
# Risk: MEDIUM
- name: Reboot Host
hosts: "{{ target_host }}"
become: yes
gather_facts: no
vars:
reboot_timeout: 300
tasks:
- name: Record uptime before reboot
ansible.builtin.command: uptime -s
register: uptime_before
changed_when: false
- name: Reboot the host
ansible.builtin.reboot:
reboot_timeout: "{{ reboot_timeout }}"
msg: "Automated reboot initiated by n8n remediation workflow"
- name: Record uptime after reboot
ansible.builtin.command: uptime -s
register: uptime_after
changed_when: false
- name: Verify host is responsive
ansible.builtin.ping:
- name: Set result fact
ansible.builtin.set_fact:
remediation_result:
success: true
host: "{{ target_host }}"
uptime_before: "{{ uptime_before.stdout }}"
uptime_after: "{{ uptime_after.stdout }}"
message: "Host {{ target_host }} rebooted successfully. Was up since {{ uptime_before.stdout }}, now up since {{ uptime_after.stdout }}"
- name: Output result
ansible.builtin.debug:
var: remediation_result
Playbook: kill-process.yml
---
# Kill a runaway process
# Variables: target_host, process_name or process_pid, signal (optional, default TERM)
# Risk: MEDIUM
- name: Kill Runaway Process
hosts: "{{ target_host }}"
become: yes
gather_facts: no
vars:
kill_signal: "{{ signal | default('TERM') }}"
use_pid: "{{ process_pid is defined and process_pid | string | length > 0 }}"
use_name: "{{ process_name is defined and process_name | string | length > 0 }}"
tasks:
# Input validation
- name: Validate that at least one target is provided
ansible.builtin.assert:
that:
- use_pid | bool or use_name | bool
fail_msg: "Either process_name or process_pid must be provided"
- name: Validate process_name contains only safe characters
ansible.builtin.assert:
that:
- process_name is regex('^[a-zA-Z0-9._:/@*? -]+$')
fail_msg: "Invalid process name '{{ process_name }}' - contains disallowed characters"
when: use_name | bool
- name: Validate process_pid is numeric
ansible.builtin.assert:
that:
- process_pid | string is regex('^[0-9]+$')
fail_msg: "Invalid PID '{{ process_pid }}' - must be numeric"
when: use_pid | bool
- name: Validate kill signal
ansible.builtin.assert:
that:
- kill_signal is regex('^[A-Z0-9]+$')
fail_msg: "Invalid signal '{{ kill_signal }}'"
# Discover PIDs
# When a PID is provided, use it directly. When only a name is given,
# find matching PIDs. Never do both - PID takes precedence.
- name: Find PIDs by process name
ansible.builtin.shell: >
pgrep -x '{{ process_name }}' | head -5
register: found_pids
changed_when: false
failed_when: false
when: use_name | bool and not (use_pid | bool)
- name: Fall back to full command-line match if exact match found nothing
ansible.builtin.shell: >
pgrep -f '{{ process_name }}' | head -5
register: found_pids_fuzzy
changed_when: false
failed_when: false
when:
- use_name | bool
- not (use_pid | bool)
- found_pids.stdout_lines | default([]) | length == 0
# Determine if process of PID is to be used
- name: Set target PIDs
ansible.builtin.set_fact:
pids_to_kill: >-
{{
[process_pid | string] if (use_pid | bool)
else (found_pids.stdout_lines | default([]))
if (found_pids.stdout_lines | default([]) | length > 0)
else (found_pids_fuzzy.stdout_lines | default([]))
}}
# Fail-safe
- name: Fail if no matching processes found
ansible.builtin.fail:
msg: >-
No processes found matching
{{ ('PID ' + process_pid | string) if (use_pid | bool)
else ('name "' + process_name + '"') }}
on {{ target_host }}
when: pids_to_kill | length == 0
# Capture state before kill
- name: Get process details before kill
ansible.builtin.shell: >
ps -p {{ pids_to_kill | join(',') }} -o pid,user,%cpu,%mem,start,command --no-headers 2>/dev/null || true
register: process_details
changed_when: false
# Kill the process
- name: Send signal to target PIDs
ansible.builtin.shell: "kill -{{ kill_signal }} {{ item }}"
loop: "{{ pids_to_kill }}"
register: kill_results
failed_when: false
# Verify - adjust as per your needs
- name: Wait for processes to terminate
ansible.builtin.pause:
seconds: 9
- name: Check if PIDs are still running
ansible.builtin.shell: "ps -p {{ pids_to_kill | join(',') }} -o pid= 2>/dev/null | wc -l"
register: remaining
changed_when: false
failed_when: false
- name: Escalate to SIGKILL if TERM did not work
ansible.builtin.shell: "kill -KILL {{ item }}"
loop: "{{ pids_to_kill }}"
when:
- remaining.stdout | default('0') | trim | int > 0
- kill_signal == 'TERM'
register: kill_escalation
failed_when: false
- name: Wait after SIGKILL escalation
ansible.builtin.pause:
seconds: 2
when:
- remaining.stdout | default('0') | trim | int > 0
- kill_signal == 'TERM'
- name: Final verification
ansible.builtin.shell: "ps -p {{ pids_to_kill | join(',') }} -o pid= 2>/dev/null | wc -l"
register: final_remaining
changed_when: false
failed_when: false
- name: Set result fact
ansible.builtin.set_fact:
remediation_result:
success: "{{ final_remaining.stdout | default('0') | trim | int == 0 }}"
host: "{{ target_host }}"
process: "{{ process_name | default(process_pid | string) }}"
pids_killed: "{{ pids_to_kill }}"
signal_sent: "{{ kill_signal }}"
escalated_to_kill: "{{ (remaining.stdout | default('0') | trim | int > 0) and kill_signal == 'TERM' }}"
details_before: "{{ process_details.stdout | default('N/A') }}"
message: >-
{{
'Process ' + (process_name | default(process_pid | string))
+ ' (PIDs: ' + (pids_to_kill | join(', '))
+ ') killed successfully with ' + kill_signal
+ (' (escalated to SIGKILL)' if ((remaining.stdout | default('0') | trim | int > 0) and kill_signal == 'TERM') else '')
if (final_remaining.stdout | default('0') | trim | int == 0)
else 'Process ' + (process_name | default(process_pid | string))
+ ' may still be running after ' + kill_signal + ' + SIGKILL signals'
}}
- name: Output result
ansible.builtin.debug:
var: remediation_result
File: README.md
- Written by Claude 4.6 based on my notes and code analysis
Add Jobs To Your Automation Platform
In AWX:
- Sync your source version control tool with AWX (Resources → Projects → click on the ‘Sync’ button) – assuming you have this set up already.
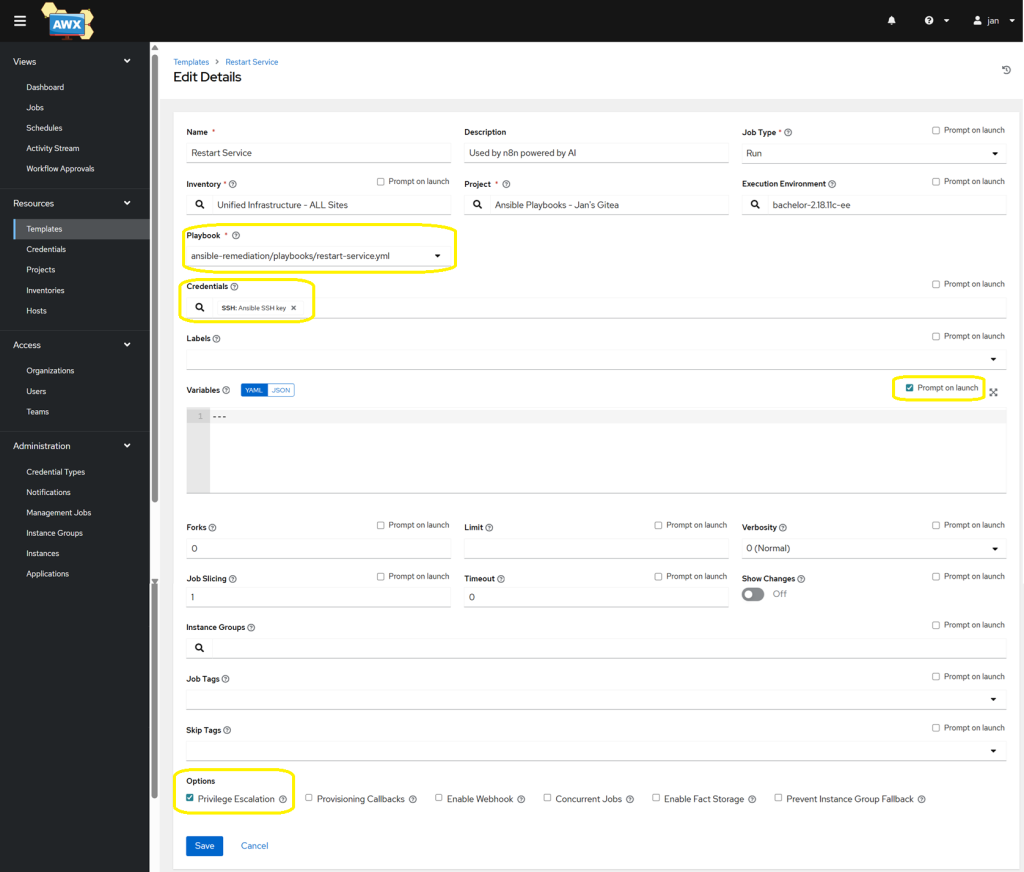
- Add the 4 jobs – one for each template.
- Ensure you tick the box near the Variables section called ‘Prompt on launch’, so that n8n can pass
target_hostandservice_name. - Similarly, tick the box called ‘Privilege Escalation’ to grant
sudopermissions (this may not be required if your ansible credential already hasbecomeconfigured with a password method).
- Ensure you tick the box near the Variables section called ‘Prompt on launch’, so that n8n can pass
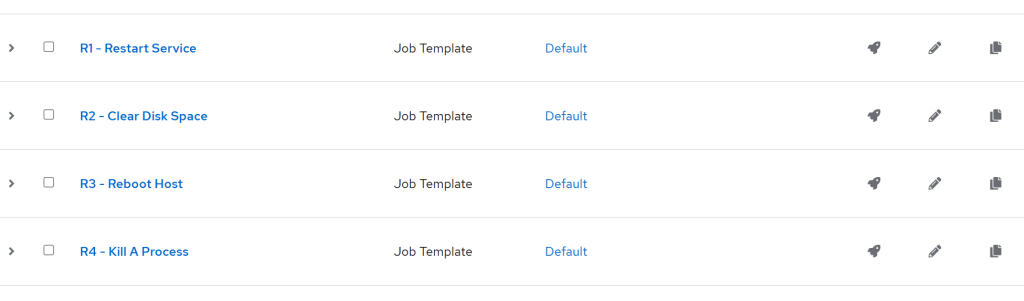
- Once you add all four, note their IDs (as per their URL). In my case, these are:
- R1 – Restart Service – ID:
38 - R2 – Clear Disk Space – ID:
39 - R3 – Reboot Host – ID:
40 - R4 – Kill A Process – ID:
41 - (Note: R stands for Remedy)
- R1 – Restart Service – ID:
- As for Semaphore UI:
- Go to your project → Task Templates.
- The template ID is visible in the URL when you click on a template, such as:
https://your-semaphore/project/1/templates/5→ in this example, the template ID is number 5 and the project ID is 1. - Enter both values in the Config node.
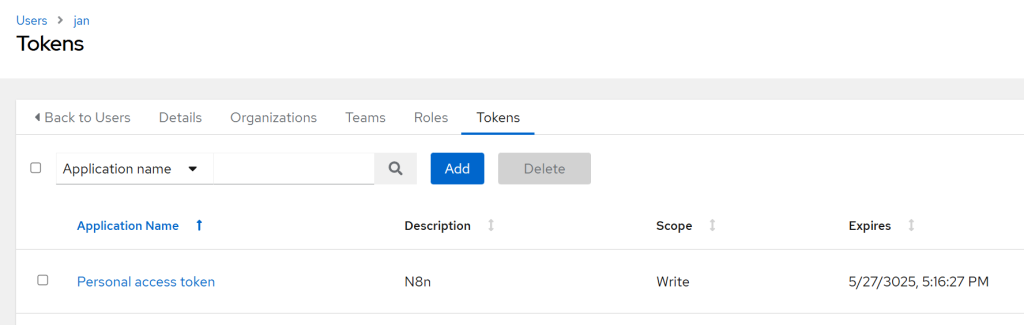
Create an API Token
This is to ensure that n8n can reach your automation platform of choice.
- In AWX, go to Users → your user → Tokens → Add
- Scope:
Write(leave the Application field empty)- Copy the token to your password manager to be used once we import the workflow.
With the automated templates being set up, there is one more step we need to do before importing the actual workflow – a Discord bot needs to be configured. This is because of the introduction of an approval workflow that we will introduce into the workflow – to maintain control while valuing AI-assisted automation.