Relevant documentation: mariadb-backup SST method
Later on, once your Galera cluster is operational, your nodes will exchange data using these two types of syncs:
- IST is used when a node has only been offline for a short time. It just asks for the missing transactions from the donor’s cache (
gcache). - SST is a full copy of the entire dataset, which is what invokes the
wsrep_sst_methodscript (mariabackuporrsync).
Methods of syncing:
- Previously,
rsyncwas the method used for syncing between nodes. The challenge with this method is that while the update is being sent by the ‘donor’ node, the receiving ‘joiner’ node is not accepting other traffic. - With the mariadb-backup method, traffic is still being accepted even while the sync is in progress. This is achieved by using a
socatutility, which must be installed on both ‘donor’ and the ‘joiner’ nodes.
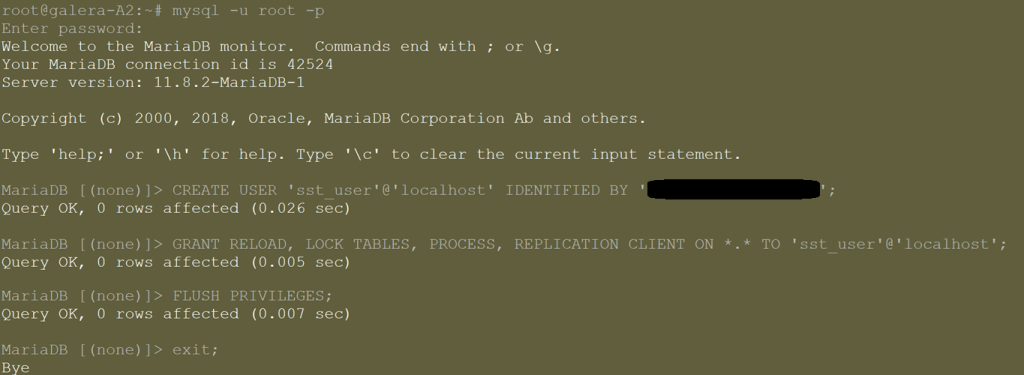
We will need to create a user in MariaDB with a password on all future nodes in our cluster, so let’s do it on the template.
# Log into your MariaDB instance mariadb -u root -p CREATE USER 'sst_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'YourSuperSecurePassword'; GRANT RELOAD, LOCK TABLES, PROCESS, REPLICATION CLIENT ON *.* TO 'sst_user'@'localhost'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; EXIT;
- A Security Note: The password for the SST user should be very strong, as it has extensive privileges on the database. There are different ways of how you can authenticate (see MariaDB’s documentation). When using the unix method of authentication (this is our case), the password is stored in plain-text in a configuration file. In our case, in step 7, it will be stored in
/etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/60-galera.cnf. Ensure that you have proper file permissions set to prevent unauthorized access.