While you could tackle it manually, if you have AWX (or Semaphore or pure Ansible) deployed in your home lab, you can create a playbook and tackle it for all your hosts, which is very elegant and future-proof.
- If you do not have such an automation in place and you find it interesting, why don’t you set up AWX using my previous guide? See Deploy Ansible AWX to automate OS patching.
- For AWX, you will need space for source control in your own repo. I’m using a locally hosted Gitea.
Playbook structure
Here is the structure of the repo. This structure follows standard Ansible best practices for role-based playbooks. It may feel like a lot of files/folders, yet each has a slightly different role and is kept as short as possible, so do not feel discouraged. Rather, let’s dive into each.
alloy-deploy/ ├── playbook.yml ├── inventory/ │ └── group_vars/ │ └── all.yml ├── roles/ │ └── alloy/ │ ├── tasks/ │ │ └── main.yml │ ├── templates/ │ │ └── config.alloy.j2 │ ├── handlers/ │ │ └── main.yml │ └── files/ │ └── alloy.service
Initial playbook
In this playbook, we confirm the OS family of the host that is being processed.
- If it is the one(s) we want, the ‘alloy’ role is assumed and additional scripts are triggered in the
/roles/alloy/folder. - If it is not the supported OS architecture, then the playbook reports it and does not proceed further for the given host.
- Replace the
monitoring_serverIP with the IP of your VM on which you installed the Docker containers.
# playbook.yml
---
- name: Deploy Grafana Alloy monitoring agent
hosts: all
become: true
vars:
monitoring_server: "1.2.3.4"
alloy_version: "1.8.2"
pre_tasks:
- name: Gather OS facts if not already present
ansible.builtin.setup:
gather_subset:
- '!all'
- os_family
when: ansible_os_family is not defined
- name: Check if host is supported
ansible.builtin.set_fact:
alloy_supported: "{{ ansible_os_family == 'Debian' and 'no_monitoring' not in group_names }}"
- name: Skip unsupported or excluded hosts
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: >-
Skipping {{ inventory_hostname }} -
{% if 'no_monitoring' in group_names %}excluded via no_monitoring group
{% else %}OS family {{ ansible_os_family }} not supported{% endif %}
when: not alloy_supported
roles:
- role: alloy
when: alloy_supported
The main task
After the pre-check is passed, the main playbook is triggered.
- The variable
host_siteis defined based on group membership – if you do not have those defined, either remove this task or modify it to your liking. - The playbook verifies that an installation of the agent is even needed and if yes, it is downloaded, unzipped, installed, permissions set and Alloy is added to
systemdto be managed as a service (daemon) and to start at boot time. Lastly, the downloaded zipped binary and extracted data are deleted.
# roles/alloy/tasks/main.yml
---
- name: Check if Alloy is already installed
ansible.builtin.stat:
path: /usr/local/bin/alloy
register: alloy_binary
- name: Get installed Alloy version
ansible.builtin.command: /usr/local/bin/alloy --version
register: alloy_installed_version
changed_when: false
failed_when: false
when: alloy_binary.stat.exists
- name: Set install required fact
ansible.builtin.set_fact:
alloy_install_required: "{{ not alloy_binary.stat.exists or (alloy_version not in (alloy_installed_version.stdout | default(''))) }}"
- name: Install dependencies
ansible.builtin.apt:
name:
- unzip
- curl
state: present
update_cache: true
when: alloy_install_required
- name: Download Alloy
ansible.builtin.get_url:
url: "<https://github.com/grafana/alloy/releases/download/v>{{ alloy_version }}/alloy-linux-amd64.zip"
dest: "/tmp/alloy-linux-amd64.zip"
mode: '0644'
when: alloy_install_required
- name: Extract Alloy binary
ansible.builtin.unarchive:
src: "/tmp/alloy-linux-amd64.zip"
dest: "/tmp/"
remote_src: true
when: alloy_install_required
- name: Install Alloy binary
ansible.builtin.copy:
src: "/tmp/alloy-linux-amd64"
dest: "/usr/local/bin/alloy"
mode: '0755'
remote_src: true
when: alloy_install_required
notify: Restart Alloy
- name: Create config directory
ansible.builtin.file:
path: /etc/alloy
state: directory
mode: '0755'
- name: Create data directory
ansible.builtin.file:
path: /var/lib/alloy
state: directory
mode: '0755'
- name: Determine site from group membership
ansible.builtin.set_fact:
host_site: >-
{%- if 'site1' in group_names -%}site1
{%- elif 'site3' in group_names -%}site2
{%- elif 'site3' in group_names -%}site3
{%- else -%}unknown
{%- endif -%}
- name: Deploy Alloy configuration
ansible.builtin.template:
src: config.alloy.j2
dest: /etc/alloy/config.alloy
mode: '0644'
notify: Restart Alloy
- name: Deploy systemd service
ansible.builtin.copy:
src: alloy.service
dest: /etc/systemd/system/alloy.service
mode: '0644'
notify:
- Reload systemd
- Restart Alloy
- name: Enable and start Alloy
ansible.builtin.systemd:
name: alloy
enabled: true
state: started
daemon_reload: true
- name: Clean up downloaded files
ansible.builtin.file:
path: "{{ item }}"
state: absent
loop:
- /tmp/alloy-linux-amd64.zip
- /tmp/alloy-linux-amd64
when: alloy_install_required
Deploy config file for alloy
Apart from the installation of Alloy for each host, we will also want to deploy a config file so that it knows about where the Prometheus server is and what hostname should Loki use (which we take from the actual hostname in Ansible).
Apart from a variable called host_site defined in the previous template, there is another variable expected to be present for you to have defined for each host:
ansible_host— either the IP or the FQDN
If you do not have it defined, check out my previous tutorial or try adding it or adjusting the script below, whatever works for you 😇
Feel free to add/remove services as you need per your own environment.
See below for the content of the config.alloy.j2 file:
// Grafana Alloy Configuration
// Managed by Ansible - do not edit manually
// Host: {{ ansible_host }}
// Site: {{ host_site }}
prometheus.exporter.unix "local" {
enable_collectors = ["cpu", "diskstats", "filesystem", "loadavg", "meminfo", "netdev", "systemd", "pressure"]
systemd {
enable_restarts = true
unit_include = "(mariadb|mysql|nginx|apache2|docker|sshd|alloy|proxmox-backup-proxy|pveproxy|pvedaemon|corosync|gitea|postfix|dovecot|fail2ban|syncthing@.*)\\\\.service"
}
}
prometheus.exporter.process "default" {
matcher {
{% raw %}
name = "{{.Comm}}"
{% endraw %}
cmdline = [".+"]
}
}
discovery.relabel "unix" {
targets = prometheus.exporter.unix.local.targets
rule {
target_label = "instance"
replacement = "{{ ansible_host.split('.')[0] }}"
}
}
discovery.relabel "process" {
targets = prometheus.exporter.process.default.targets
rule {
target_label = "instance"
replacement = "{{ ansible_host.split('.')[0] }}"
}
}
prometheus.scrape "unix" {
targets = discovery.relabel.unix.output
forward_to = [prometheus.remote_write.default.receiver]
scrape_interval = "30s"
job_name = "integrations/unix"
}
prometheus.scrape "process" {
targets = discovery.relabel.process.output
forward_to = [prometheus.remote_write.default.receiver]
scrape_interval = "30s"
job_name = "integrations/process"
}
{% if 'docker' in group_names %}
prometheus.exporter.cadvisor "docker" {
docker_host = "unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
docker_only = true
}
discovery.relabel "docker" {
targets = prometheus.exporter.cadvisor.docker.targets
rule {
target_label = "instance"
replacement = "{{ ansible_host.split('.')[0] }}"
}
}
prometheus.scrape "docker" {
targets = discovery.relabel.docker.output
forward_to = [prometheus.remote_write.default.receiver]
scrape_interval = "30s"
job_name = "integrations/docker"
}
{% endif %}
prometheus.remote_write "default" {
endpoint {
url = "http://{{ monitoring_server }}:9090/api/v1/write"
}
external_labels = {
host = "{{ ansible_host }}",
site = "{{ host_site }}",
}
}
loki.source.journal "systemd" {
forward_to = [loki.process.add_labels.receiver]
relabel_rules = loki.relabel.journal.rules
labels = { job = "systemd-journal" }
}
loki.relabel "journal" {
forward_to = []
rule {
source_labels = ["__journal__systemd_unit"]
target_label = "unit"
}
rule {
source_labels = ["__journal_priority_keyword"]
target_label = "level"
}
}
loki.source.file "varlogs" {
targets = [
{ __path__ = "/var/log/*.log", job = "varlogs" },
{ __path__ = "/var/log/**/*.log", job = "varlogs" },
]
forward_to = [loki.process.add_labels.receiver]
}
loki.process "add_labels" {
forward_to = [loki.write.default.receiver]
stage.static_labels {
values = {
host = "{{ ansible_host }}",
instance = "{{ ansible_host.split('.')[0] }}",
site = "{{ host_site }}",
}
}
}
loki.write "default" {
endpoint {
url = "http://{{ monitoring_server }}:3100/loki/api/v1/push"
}
}
Systemd unit file for Alloy
The content of the alloy.service file used for systemd:
# roles/alloy/files/alloy.service [Unit] Description=Grafana Alloy After=network.target [Service] Type=simple ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/alloy run /etc/alloy/config.alloy --storage.path=/var/lib/alloy Restart=always RestartSec=5 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Service restart handlers
This short playbook handles the reloading of the systemd daemon and the restarting of the alloy service after Alloy is installed.
# roles/alloy/handlers/main.yml
---
- name: Reload systemd
ansible.builtin.systemd:
daemon_reload: true
- name: Restart Alloy
ansible.builtin.systemd:
name: alloy
state: restarted
Docker Monitoring server info
This is optional but recommended — these are default variables shared across all hosts (monitoring server IP, Alloy agent version).
# inventory/group_vars/all.yml --- monitoring_server: "your_actual_vm_ip" alloy_version: "1.8.2" # Replace this with your current version
Sync Playbook and add a template
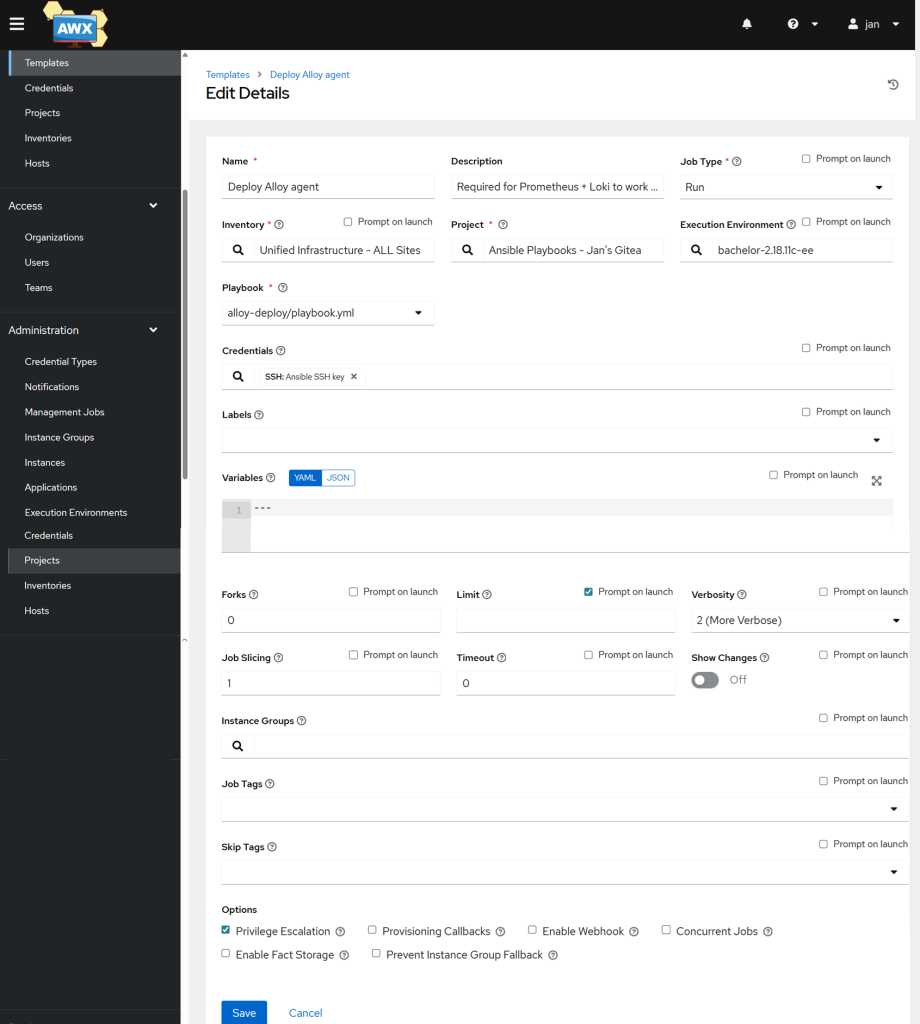
Once all the files are uploaded to your preferred source version control software, go to Projects and click on the sync button to sync the newest addition with your AWX instance.
Then head to Templates → Add button → Add job template.
- Name: Deploy Alloy agent
- Inventory: your inventory – best to have it all under one unified one with all sites
- Project: Your source version controlled repo
- Execution Environment: your preferred EE that has at least the
ansible.netcommonlibrary. See more info on how to set up your own EE. - Playbook: Choose the playbook we created above
- Credentials: All your hosts need to be reachable via SSH, choose a credential
- Tick the box for Privilege Escalation
Run the job on just one or a few hosts before running it on the whole fleet. Then watch and enjoy 😇
Ensure data is flowing to Grafana
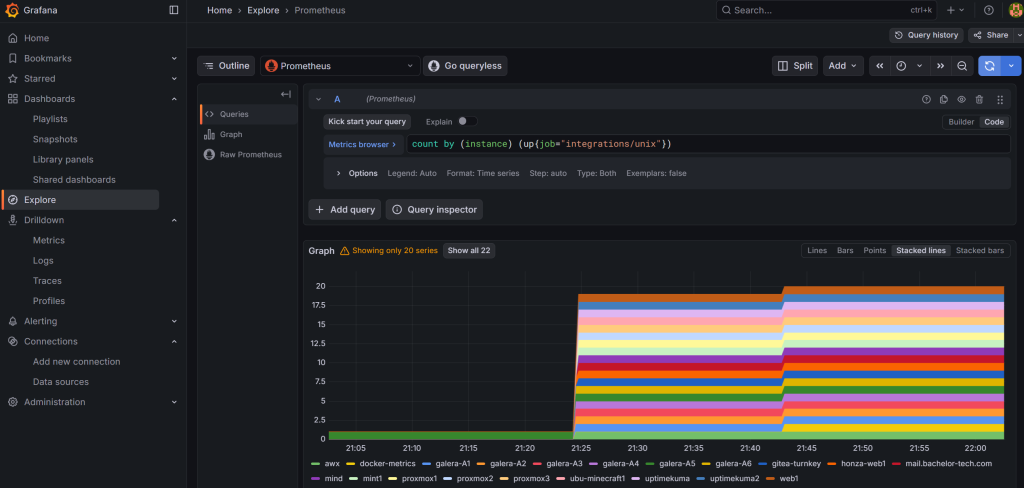
Let’s confirm that the data is actually present in Grafana.
Go to Explore → select Prometheus → run this query (use the ‘code’ view to just copy paste the command below):
count by (instance) (up{job="integrations/unix"})
The result should not surprise you – based on the number of successful completions in AWX:
With hosts being added, we can now consider customizing our dashboard to see what we want to see.